Low-code development
Rapid Application Development:
where low-code platforms come to life
Written by:

Rano Salieva
Posted on:
14.02.2025
Reading Time:
5 min
In a nutshell
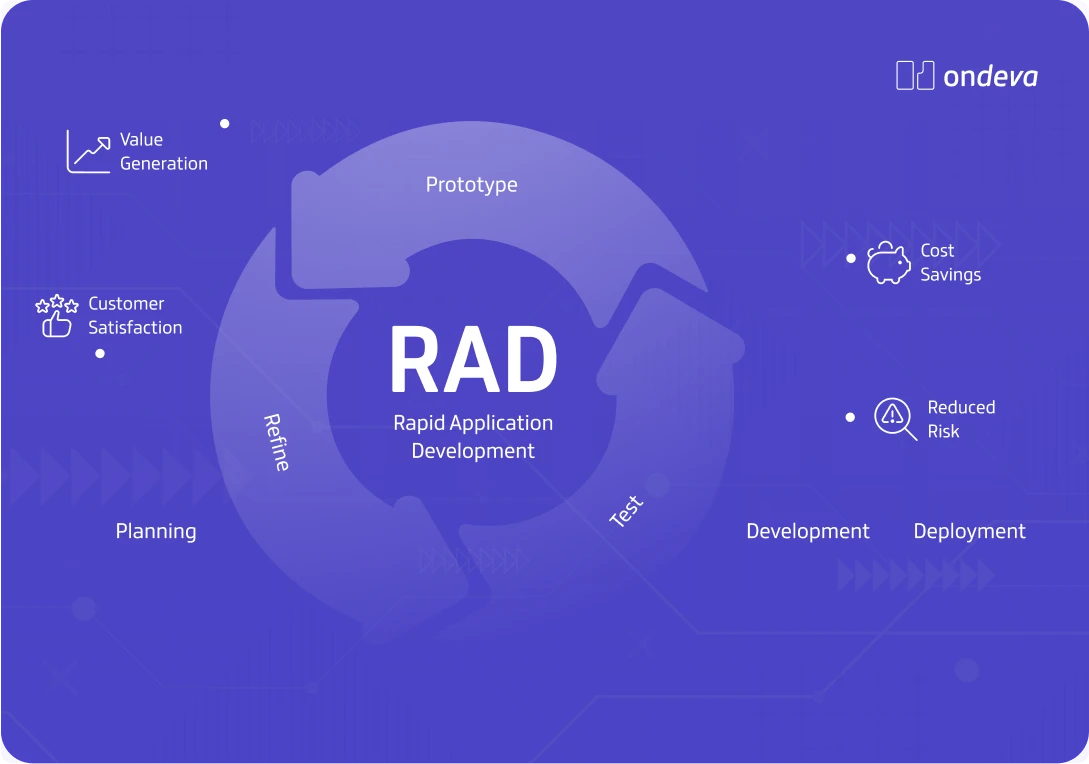
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a way to make software fast and flexibly. It's like having a quick chat instead of sending letters: you build a bit, get feedback, and improve it, over and over. This method is perfect for projects that need to be done quickly or might change a lot.
The process has five steps: figuring out what the business needs, planning how data is used, designing how things will work, building the app, and then testing and fixing it.
Ready to build an app without all the fuss? Ondeva lets you dive in for free. You'll find everything you need to get going and can see your app take shape in no time. Start building today and bring your ideas to life!
What is rapid application development?
Before we bring low-code platforms into this conversation, let’s get clear on what Rapid Application Development is, why developers choose it, and when it’s most commonly used.
Defining rapid application development
The rapid application development model (RAD) is a software development methodology that relies on quick development, feedback and iteration loops instead of linear timelines.
RAD prioritizes resources towards prototyping based on user testing, rather than planning. In traditional models, users are involved at the very start and end. In RAD, they are integral to almost all stages of development.
If traditional development cycles can be compared to writing a long letter and sending it by post, RAD is more like a back-and-forth phone call.
Use cases for rapid application development
Some of the most common reasons teams use the rapid application development methodology include:
- Developing internal tools
- Projects with short timelines
- Products with experienced users
- Projects with a broad or evolving brief
Typically, RAD is faster and cheaper than traditional development models. It’s popular with teams of limited resources, tight deadlines or multiple projects.
Understanding the phases of rapid application development
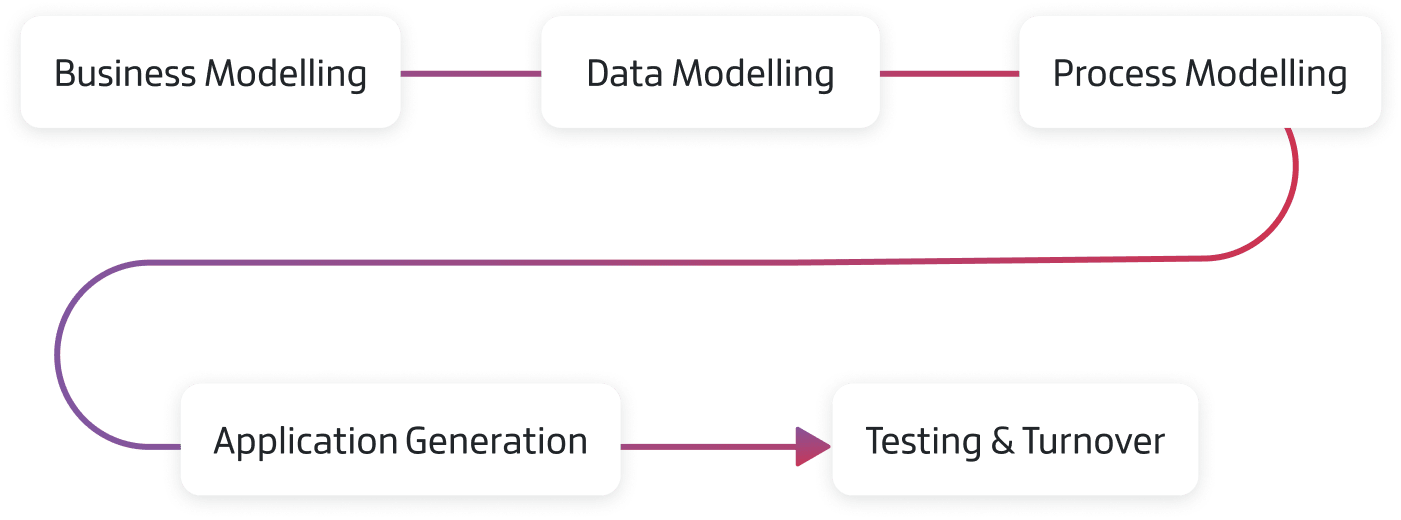
There are five distinct phases to the RAD model. Some developers might use different terminology, but the purpose of each phase is usually the same.
The five phases of RAD in detail
1. Business Modelling
The first phase of Rapid Application Development is to understand the needs, requirements, and data flows within the business. This phase establishes the guard rails for the project, ensuring that what is built is relevant.
In this phase, user roles will also be established. For example: administrators, customers, and guest users.
The team may develop flowcharts and maps at this stage, to model common behaviors for different user roles.
2. Data Modelling
Data modeling is a crucial phase of Rapid Application Development. In this stage, the developers identify, design, and structure the data used within the system.
As well as identifying individual entities, the developers will also scope out their relationships and interactions. For example, a user (one data entity) creating and saving a file (another data entity).
The developers will also work on subcategorization and adding data attributes (e.g. user name and user profile photo) to ensure each entity behaves as users expect.
3. Process Modelling
In the process modeling phase, the development team will map out the expected flow of data and interactions between entities. A lot of this work will be on modifying, creating, and retrieving data entities.
Process modeling gives the developers a scope of what needs to be built, according to the needs of the users and within the confines of the data available.
Another key part of this process is deciding upon the logic and rules used within the application, which will be the foundation of automations and interactions in the live app.
4. Application Generation
In this phase, the developers start developing. The aim here is to build quickly, efficiently, and with components that are easy to iterate upon.
Components and modules - whether for UI (e.g. buttons) or UX (e.g. automations) - are crucial in Rapid Application Development. The quick prototyping cycles are dependent on pre-coded elements that can be added, removed, or adapted at speed.
As well as building the UI, the developers will need to make sure the data flows work as intended and that no steps are missing.
5. Testing & Turnover
Testing and turnover are the crux of RAD. It might be rapid, but this process is also measured and controlled. Changes are made quickly but incrementally, so that processes don’t break nor are new problems created.
The application is handed over to users who will start exploring and trying to use it for its intended purpose. Though their feedback is likely to be extensive, the process of responding to it is more methodical.
As the iterations continue, the application gets closer to its functioning and usable state. After further testing and prototyping, the application will be ready to be pushed live for the entire user base.
Why choose rapid application development?
Deep collaborative work
Rapid application development builds communication across business lines. Developers, designers, and stakeholders work in tandem and improve their cross-functional skills.
Ease of Maintenance
RAD projects typically use pre-built components, as found in Ondeva. Isolating these components for updates or edits is easier than rewriting large sections of bespoke code.
Speed of release
RAD lets you launch applications much faster than traditional methods. If you need to launch quickly or work on multiple projects at once, RAD can be a game-changer.
More efficient devs
RAD lets small teams build like big ones. A tight-knit dev team can deliver more projects at more regular intervals than they would be able to using other approaches.
Catching issues early
You’re more likely to identify major bugs with RAD. Users interact with the application differently to developers, so you can catch any surprises before publishing.
Better user experience
An application built using the RAD model will be highly user-focused. The app has been developed based on real user behavior, rather than assumptions or existing patterns.
blog
Fresh ideas on workflow automation and app logic
Our blog features in-depth research and practical insights on building software without writing code.
Build for free with ondeva
No infrastructure. No coding. Try ondeva today and create your first app - on us.

